Which Command Can You Enter at the Command Prompt to List All Files and Directories in the Badams
If you've been using a Mac for any length of time, yous know that it'southward more simply a pretty point-and-click, window-and-icon interface. Beneath the surface of the operating organization is an entire world that you can access only from the command line. Terminal (in your /Applications/Utilities folder) is the default gateway to that control line on a Mac. With it, instead of pointing and clicking, you lot type your commands and your Mac does your bidding.
Why would yous want to do that? For well-nigh all of your computing needs, the regular graphical user interface is plenty. But the control line can be handy when information technology comes to troubleshooting your Mac, to plough on "hidden" settings, and other advanced chores. It's a adept idea for anyone who isn't an utter beginner to be familiar with it.
If y'all aren't already familiar with your Mac's control-line interface. First upwardly: How to navigate the file system from the control-line prompt.
The prompt
By default, when you lot open up Terminal, the first thing y'all'll meet is something like this:
Final login: Fri Jun 25 ten:37:06 on ttys000
romansempire@Mac-Pro-8 ~ %
Hither'south what you're seeing:
- The showtime line shows the concluding fourth dimension you logged into your Mac via the command line; that'south the current time, when yous're using Last.
- The second line is the prompt, and while it can alter from system to arrangement depending on configuration, past default it contains several $.25 of data:
- In the prompt above romansempire is the user name.
- Mac-Pro-8 is the name of the Mac (aforementioned as the Computer Proper name in the Sharing pane of System Preferences).
- The ~ shows where you are in the file system of the Mac. ~ is a shortcut that means the current user'southward Home folder. (In the Finder, that'due south the folder with your user name and the firm icon.)
- The % is a character that the vanquish (the default interface that Terminal uses) displays to indicate that it'due south ready to accept a command.
How to meet what's in a folder
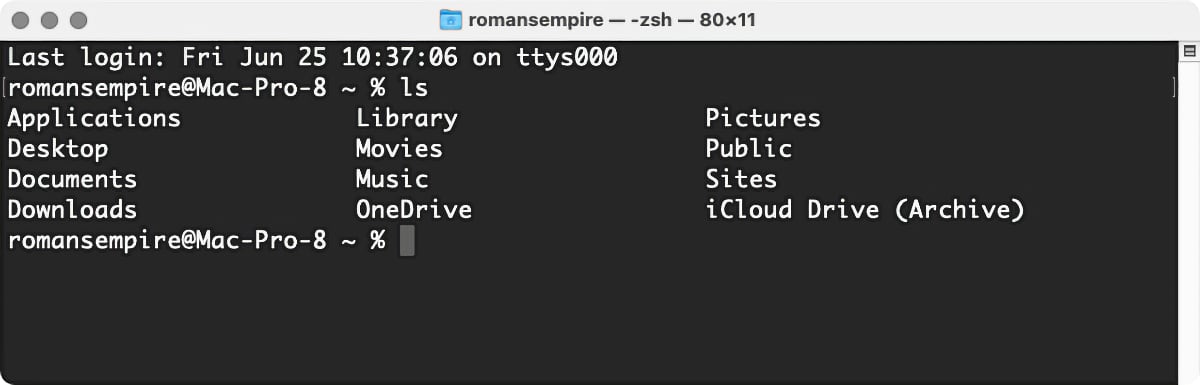
When y'all first become to the control line, you lot're in your home folder. While y'all're at that place—or when you're in any binder (directory in Unix-speak)—you might desire to know what'due south in information technology. To practise that you use the ls (or list) command. Blazon ls and press the Return key, and y'all'll run across the folders (and/or files) in the current directory.
IDG
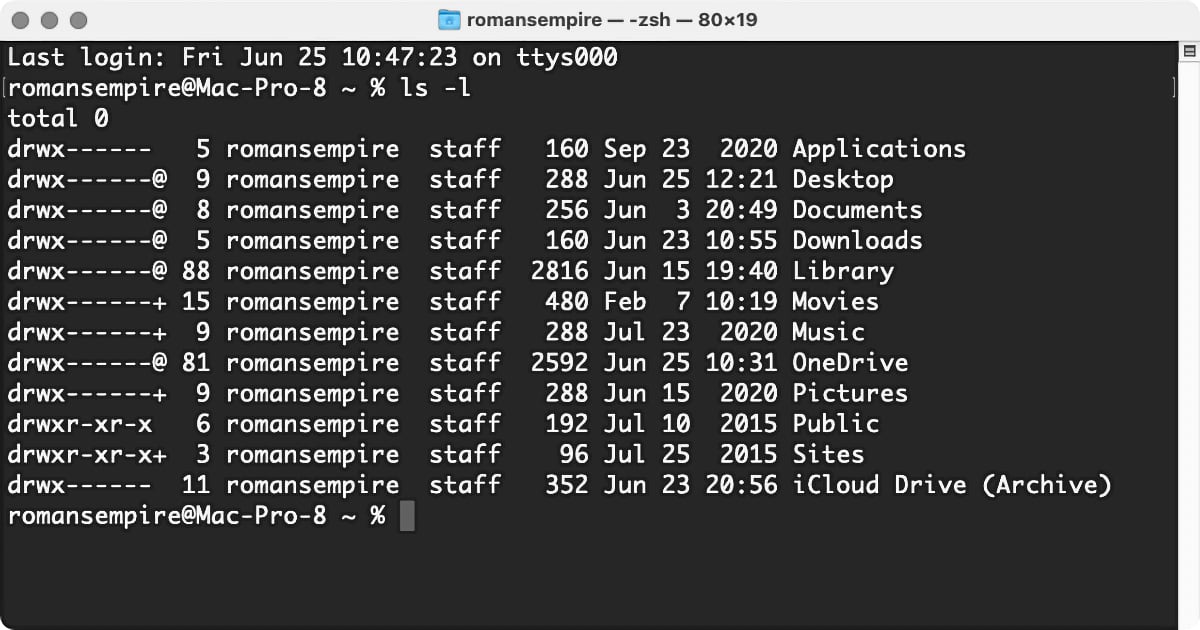
The output of the plain ls command is pretty thin; information technology shows you the names of files and folders independent in the electric current directory (including some familiar ones such as Movies, Music, Pictures, and and so on). Fortunately, you can add together a number of optional switches to the ls command that allow yous to encounter more than information. For example, type ls -fifty (that'southward a lower-case 50), then press Return. Y'all'll see something similar this:
IDG
Don't worry too much about what all that means right now—we're but getting our feet wet. The point is that ls can provide additional information nearly files and folders, depending on the options yous specify. In this instance, that boosted information includes the proper name of the user who owns each detail in the directory. (That ownership is part of the Unix system'due south file-permissions regime.) The romansempire staff next to most of those items above means that each one is owned by the user romansempire, who is in the group staff. The other understandable bit of information next to each file and folder is the date and time each one was last modified.
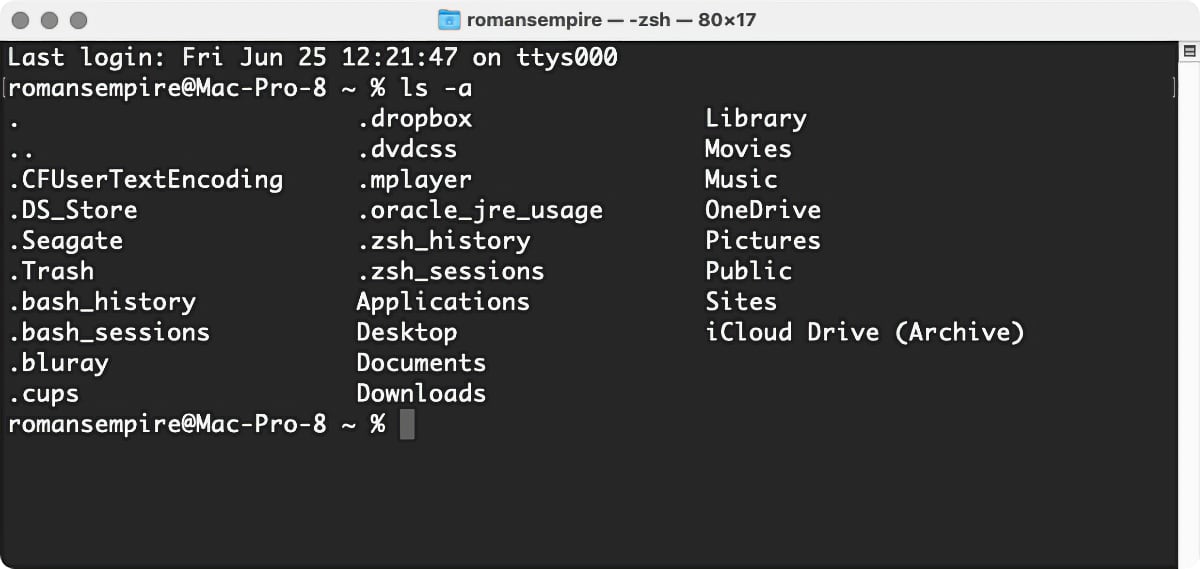
One other handy pick: You can view invisible files—ones that the Finder doesn't normally show you—by typing ls -a . (These hidden files all accept dots (.) in front of their names.)
IDG
How to access other folders/directories
When y'all're in the Finder and you want to movement to another folder, y'all find that folder and double-click it. From the command line, yous use the cd (or change directory) command instead. Then permit'south say you're in your Abode binder and desire to peek within the Downloads binder. To do that, y'all'd type cd Downloads . (Retrieve to always type a infinite after any command that has an additional argument, such as the proper noun of a directory in the previous example.) Once you've washed that, ls will show you the contents of your Downloads folder.
Here are a couple of quick tricks for moving around in your Mac's file system.
- If you type
cdand press the Return key—with no directory specified—you'll go back to your Domicile folder. (You can also blazoncd ~to go there.) - If you type
cd /, you'll become to the root level of your startup disk. - If you type
cd ..(that's two periods), you'll go to the directory above the one you're currently in. And so if you're in your habitation binder, and typecd .., yous'll go to your Mac's /Users binder. - And if you type
cd -(hyphen) you'll go back to the directory you were in before the last time you issued thecdcommand.
To larn more Terminal commands, run across our articles on how to copy and move folders as well as delete files and folders using the control line and get aid when you need it from homo pages.
Note: When you buy something subsequently clicking links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. Read our chapter link policy for more details.
Kirk McElhearn (@mcelhearn) writes about Macs, music and more on his blog Kirkville. He too runs Kirk's iTunes Forum, where users can discuss iTunes, iOS devices, music, and more.
Source: https://www.macworld.com/article/221277/command-line-navigating-files-folders-mac-terminal.html
0 Response to "Which Command Can You Enter at the Command Prompt to List All Files and Directories in the Badams"
Post a Comment